HEART DISEASE
Heart Disease - What is It?
Heart disease, also called cardiovasular disease, describes a range of conditions that affect your heart. There are many diseases that are categorized as heart disease, including coronary artery disease, arrhythmias (heart rhythm problems, and congenital heart defects (heart defects you are born with), among many others.
According to the World Health Organization and the CDC, Heart Disease is the leading cause of death in the US, UK, Canada and Australia1. Currently, 26.6 million US adults (11.3% of the adult population) is diagnosed with Heart Disease. 23.5% of all deaths in the US today are caused by heart disease2.
COMMON EXAMPLES OF HEART DISEASE
Angina
Angina is chest pain or discomfort caused when your heart muscle doesn’t get enough oxygen-rich blood. It may feel like pressure or squeezing in your chest. The discomfort also can occur in your shoulders, arms, neck, jaw, or back. Angina pain may even feel like indigestion.
Arrythmia
There are various types of arrhythmias. An arrhythmia is an abnormal rhythm of the heart. The heart can beat too slow, too fast or irregularly. An arrhythmia can affect how well the heart works. The heart may not be able to pump enough blood to meet the body’s needs.
Congenital Heart Disease
Congenital Heart Disease can describe several different problems affecting the heart. It is the most common type of birth defect. CHD causes more deaths in the first year of life than any other birth defects.
Congestive Heart Failure
Congestive heart failure, occurs when your heart muscle doesn’t pump blood as well as it should. Certain conditions, such as narrowed arteries in your heart (coronary artery disease) or high blood pressure, gradually leave your heart too weak or stiff to fill and pump efficiently.
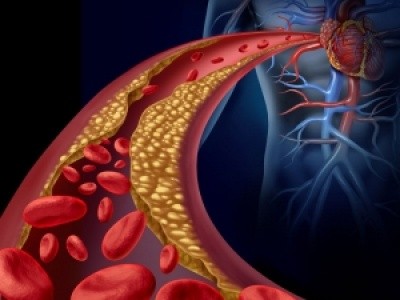
Coronary Artery Disease
Coronary artery disease (CAD) is the most common type of heart disease. It is the leading cause of death in the United States in both men and women. CAD happens when the arteries that supply blood to heart muscle become hardened and narrowed.
Dilated Cardiomyopathy
Dilated cardiomyopathy is a disease of the heart muscle, usually starting in your heart’s main pumping chamber (left ventricle). The ventricle stretches and thins (dilates) and can’t pump blood as well as a healthy heart can.
Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy
Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy occurs if heart muscle cells enlarge and cause the walls of the ventricles (usually the left ventricle) to thicken. The ventricle size often remains normal, but the thickening may block blood flow out of the ventricle. If this happens, the condition is called obstructive hypertrophic cardiomyopathy.
content goes here. Edit or remove this text inline or in the module Content settings. You can also style every aspect of this content in the module Design settings and even apply custom CSS to this text in the module Advanced settings.
Mitral Valve Prolapse
Mitral valve prolapse (MVP) occurs when one of your heart’s valves doesn’t work properly. The flaps of the valve are “floppy” and don’t close tightly. Most people who have the condition are born with it. It also tends to run in families.
Mitral Valve Regurgitation
Mitral valve regurgitation — also called mitral regurgitation, mitral insufficiency or mitral incompetence — is a condition in which your heart’s mitral valve doesn’t close tightly, allowing blood to flow backward in your heart. Thus, blood can’t move through your heart or to the rest of your body as efficiently, making you feel tired or out of breath.
Myocardial Infarction
Commonly known as a heart attack, Myocardial Infarction, occurs when blood flow stops to a part of the heart causing damage to the heart muscle. The most common symptom is chest pain or discomfort which may travel into the shoulder, arm, back, neck, or jaw. Often it is in the center or left side of the chest and lasts for more than a few minutes. The discomfort may occasionally feel like heartburn. Other symptoms may include shortness of breath, nausea, feeling faint, a cold sweat, or feeling tired.
Pulmonary Stenosis
Pulmonary Stenosis, also known as Pulmonic Stenosis, is a dynamic or fixed obstruction of flow from the right ventricle of the heart to the pulmonary artery. It is usually first diagnosed in childhood. It may occur in association with other congenital heart defects as part of more complicated syndromes.